2023 – The Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) is launched by the European Space Agency.
2015 – Dragon CRS-6 is launched to ISS on a resupply mission. Falcon 9’s first stage recovery failed. It was flown down to the barge ‘Just Read The Instructions’ in the Atlantic but a stuck valve caused control problems in the final burn and the stage crash-landed. Included in the new supplies now onboard the ISS is a 20 kg microgravity-qualified Lavazza “ISSpresso” machine.

2000 – Astronomers at Northwestern University and University of Illinois detected the first observational evidence for the remnants of hypernovae, explosions a hundred times more energetic than supernovae and the possible source of powerful gamma ray bursts (GRB), making them the most energetic events known in the Universe other than The Big Bang.
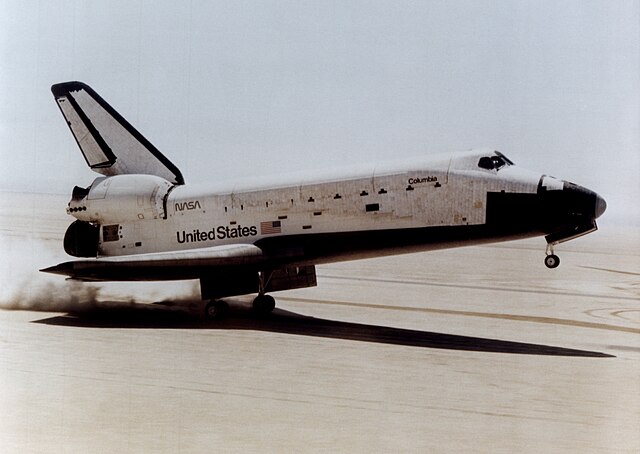
1981 – STS-1: The first operational Space Shuttle, Columbia completes its first test flight.
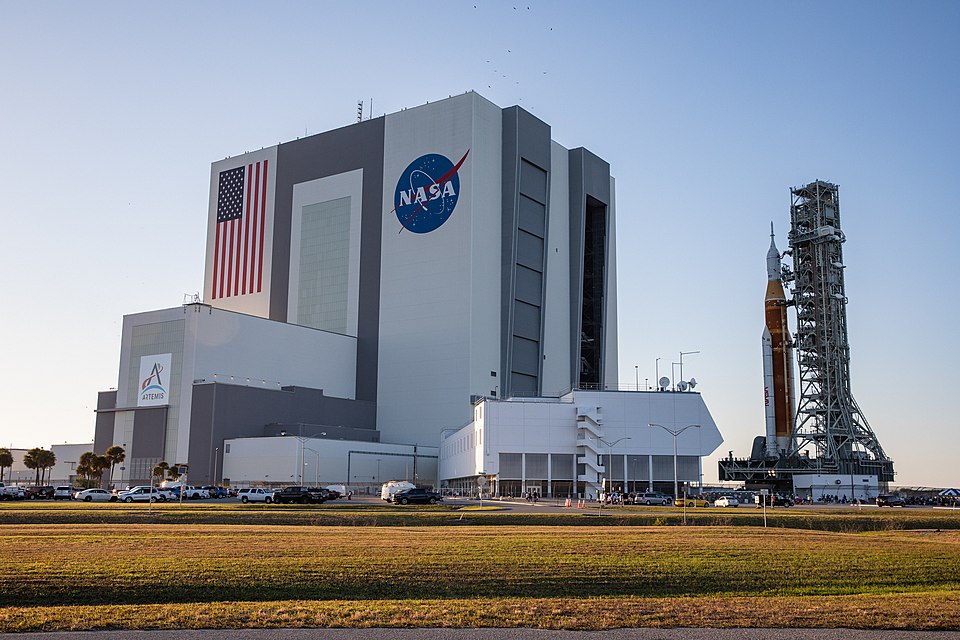
1965 -Final beam in the structural skeleton of the Vertical Assembly Building, the VAB, on Merrit Island, Kennedy Space Center was built for the Apollo Program but has gone on to service the Space Shuttle and the Artemis program. Scheduled for completion in 1966, the cavernous structure (160 m (525 ft) tall and comprising 10,968,476 cu m (129 million cu ft)) would provide a controlled environment for assembling Saturn V launch vehicles and mating them to Apollo spacecraft.

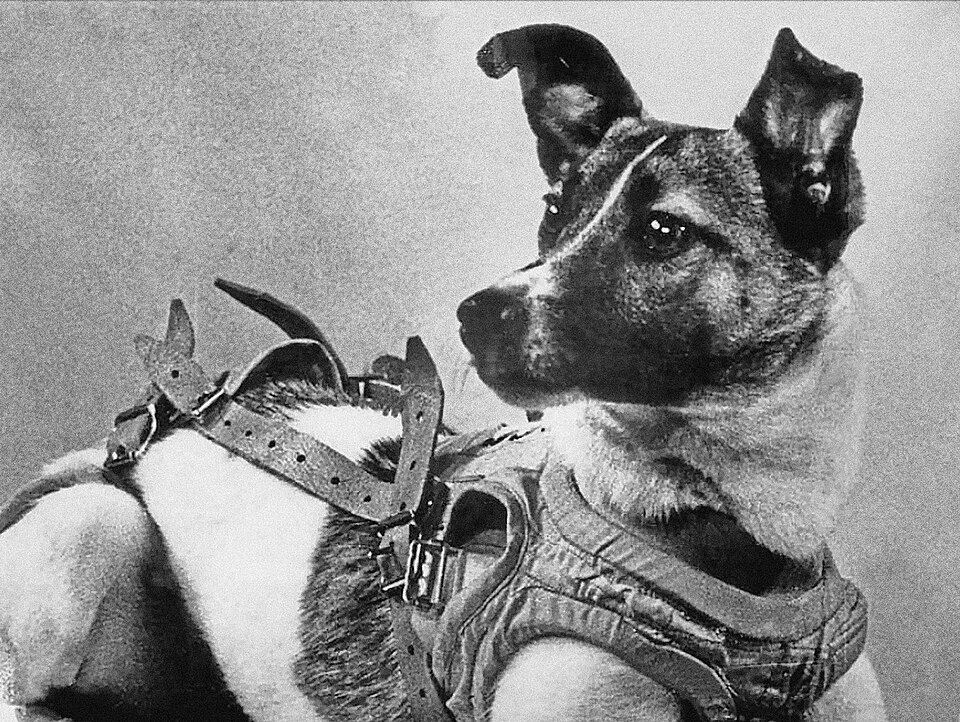
1958 – The Soviet satellite Sputnik 2 reenters after a mission duration of 162 days. This was the first spacecraft to carry a living animal, a female dog named Laika, who likely lived only a few hours.

Birthdays

1942 – Valentin Lebedev is a former Soviet cosmonaut who made two flights into space. His stay aboard the Space Station Salyut 7 with Anatoly Berezovoy in 1982, which lasted 211 days, was recorded in the Guinness Book of Records.

1629 – Christian Huygens Dutch physicist and astronomer and one of the preeminent scientists of the 17th century. Born in The Hague, The Netherlands. He studied at Leyden and Breda, discovered the ring and fourth satellite of Saturn (1655), and got the patent for the first pendulum clock (1657). In optics he propounded the wave theory of light, and discovered polarization. He lived in Paris, a member of the Royal Academy of Sciences from 1666-1681 but returned to The Hague because of religious persecution. NASA has honored Huygens by naming a space probe which is on the spacecraft Cassini, currently (1999) on its way to Saturn.